The association behaviour, modes of interaction and physico-chemical parameters of the mixture of dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide + crystal violet dye in aq. solutions of alcohols and urea: Impacts of composition and temperature
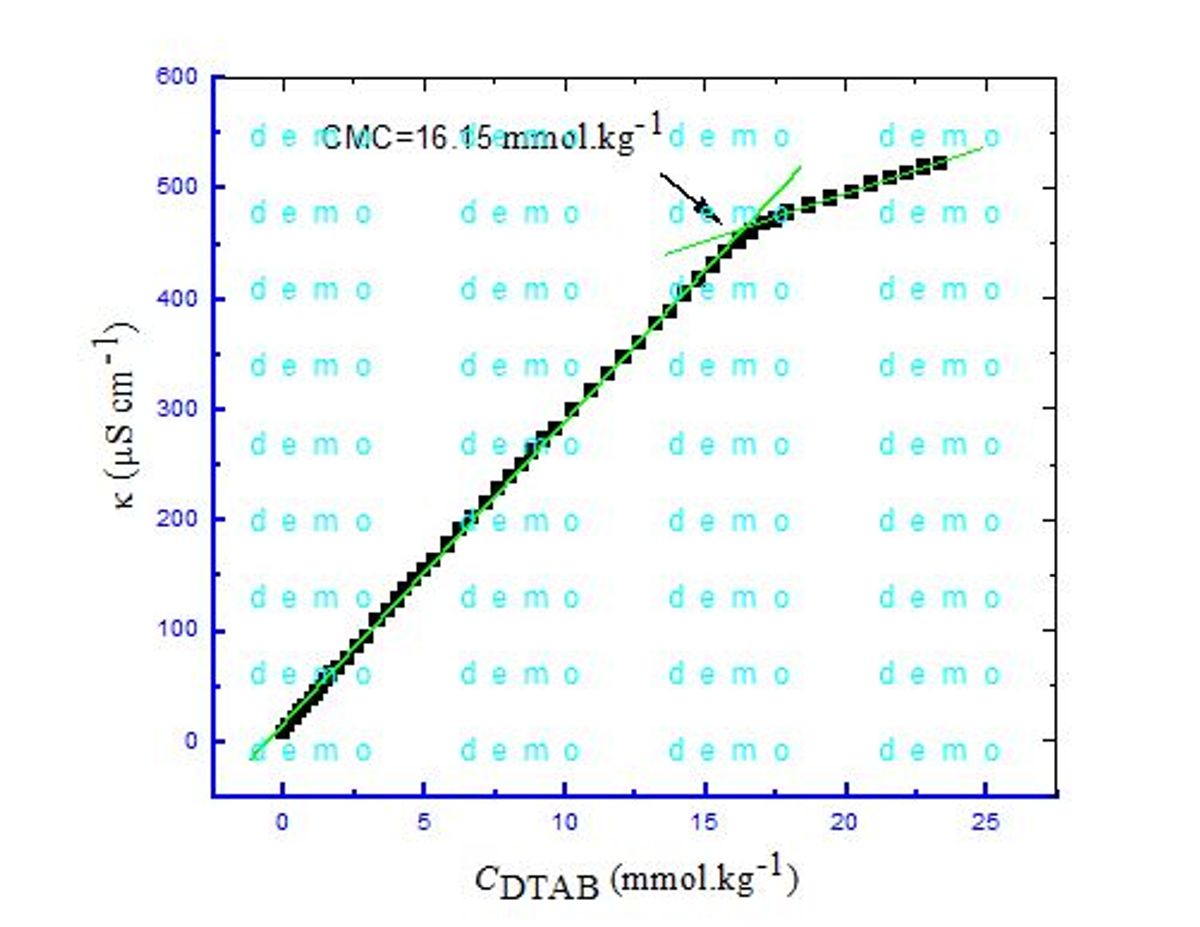
Surfactants have a crucial part in the dying process in variety of manufacturing industries especially in textiles that need an optimal adhesion of dye to fabrics. Surfactant can create such a microenvironment in system which lead to confirm better dye-to-fabric binding phenomenon. Inclusion of additives alters the interaction of dye with surfactant that might affect the binding of dye to materials. Herein, the interconnection between dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide (DTAB), a cationic surfactant, and crystal violet (CV) has been studied applying conductometric method in aq. solutions of short chain alcohols (ethanol, 1-propanol) and urea. Micellar parameter (critical micelle concentration (CMC), counter ion binding (β), degree of ionization (α)) and the thermodynamics ( , and for the assembly of DTAB + CV system were determined. For DTAB + CV micellization in presence of aqueous alcohols as well as urea medium, single break points was obtained. The values of CMC for this system are found to upsurge with the increase of concentration of alcohols and urea as well as with the increases of temperature. The values were found negative for DTAB + CV mixtures in the study media, which indicated that the micellization process was thermodynamically spontaneous. In all cases, the and values disclosed that the recommended interaction forces functioning amid DTAB and CV are the hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions.

